Internal control related to financial reporting is designed to provide reasonable assurance concerning the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, applicable laws and regulations, and other requirements covering listed companies. Risk management is considered an integral part of running Konecranes' business. Konecranes’ corporate risk management principles provide a basic framework for risk management, while each Group company or operating unit is responsible for its own risk management. This principle is also followed in risk management related to financial reporting.
Management of financial risks is described in the Note 33 of Konecranes Financial Statement 2017.
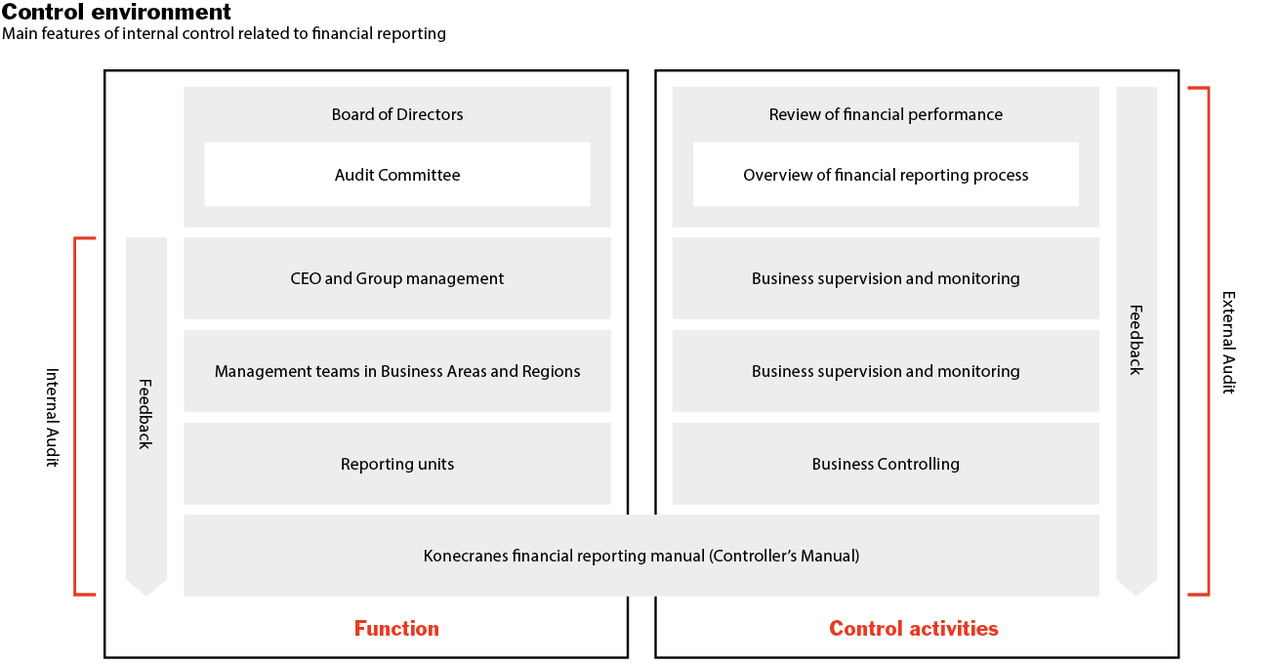
Control environment
Corporate governance and business management at Konecranes are based on the company’s values of trust in people, total service commitment, and sustained profitability. The control environment is the foundation for all the other components of internal control and for promoting employee awareness of key issues. It supports the execution of strategy and regulatory compliance. The Board of Directors and Group Management are responsible for defining the Konecranes Group’s control environment through business management structures, corporate policies, instructions, and financial reporting frameworks. These include the Konecranes Code of Conduct and the Konecranes Controller’s Manual, which constitute the main tool for accounting and financial reporting principles in respect of providing information, guidelines, and instructions. The interpretation and application of accounting standards is the responsibility of the global accounting function. Guidelines and instructions for reporting are updated when necessary and are reviewed at least once a year.
From the beginning of the year, the new business segment split was introduced, comprising three segments (business areas), Service, Industrial Equipment and Port Solutions. As a deviation to Business Area Industrial Equipment, the Business Area Port Solutions also incorporates those service branches and spare part units which are dedicated to serve the port customer segment. These units were earlier reported under the Business Area Service.
Business Area Service has three business units, Industrial Service, Parts supply and Component spare parts. Business Unit Industrial Service is internally managed and reported as a line organization through three regions - Europe, Middle East and Africa (EMEA), Americas (AME) and Asia-Pacific (APAC). Other business units are managed as line organizations globally. Business Area Industrial Equipment and Business Area Port Solutions are operated as line organizations further divided into business units and under business units further into product lines. These segments have clear product line profit responsibilities, ensuring a flawless order-delivery process and enabling effective decision making. Support functions, such as finance, legal, HR, IT and marketing and communications are managed as line organizations.
In the finance operating model, management accounting (business controlling) and financial accounting are segregated where applicable. Management accounting employees specialize in supporting the business area management decision making, whereas financial accounting primarily follows legal structure with a close link to corporate level financial accounting. Financial accounting organization also includes a separate Business Compliance team. Business Compliance is focused on supporting local units in improving controls and processes and monitoring compliance with our internal controls.
Financial targets are set and planning/follow-up activities are executed along the business area and business unit structure in accordance with the overall business targets of the Konecranes Group. The operations of the Business Area Service are typically monitored based on profit-responsible service branches, which are further consolidated to country and region levels. The Business Area Industrial Equipment is mainly monitored via Components, Industrial Cranes and Process Solutions business units, which are divided into business/product lines. Manufacturing of components, subassemblies and other parts have a separate set of KPI's, as these are treated as cost centers rather than profit-generating units. The Business Area Port Solutions has Mobile Harbor Cranes, Port Cranes, Software Solutions, Lift Trucks and Port Solutions Service business units monitored in the same way as in Business Area Industrial Equipment.
In 2017, the Group integrated all MHPS entities fully into Konecranes' operational structure. All MHPS units started to follow Konecranes' business performance methodology and reporting structure from the beginning of the year. At the same time, we maintained a parallel reporting structure enabling us to see the Konecranes legacy and MHPS legacy business performance also separately. This parallel structure will be largely dismantled from the beginning of 2018. The Konecranes control environment and activities were unified between Konecranes and MHPS legacies to the extent possible during 2017.
Control activities
Konecranes Group management has operational responsibility for internal controls. Control activities are integrated into the business processes of the Konecranes Group and management’s business supervision and monitoring procedures. Management follow-up is carried out through monthly management reporting routines and performance review meetings. These meetings are conducted at the business area and business-unit levels, based on their own management structures, as well as at the Group level. Topics covered in the meetings include a review of the sales funnel, competitive situation, market sentiment, order intake and order book, monthly financial performance, quarterly and rolling 12-month forecasts, as well as safety, people, and customer topics. The Group management separately follows up the most important development activities. For example, R&D projects are monitored by the Product Board. The Product Board convenes typically on a quarterly basis.
All legal entities and business units have their own defined controller functions. Representatives from controller functions participate in planning and evaluating unit performance, and ensure that monthly and quarterly financial reporting follows the Group’s policies and instructions and that all financial reports are delivered on time in accordance with schedules set by the Group.
The Group has identified and documented the significant internal controls that relate to its financial processes either directly or indirectly through other processes. Group companies are responsible for implementing the identified and documented internal controls. During 2017, Konecranes continued to enhance internal controls to cover identified risks more effectively in the business processes. The Group has defined a register of internal controls that apply to all entities globally. The register includes controls over assets, liabilities, revenue, and costs that require the involvement of Business and Financial Management. The register included 122 controls and are categorized as key control or operational control. The list of internal controls is reviewed annually.
Assessments and monitoring
Each legal entity/unit assesses and reports its compliance with the centrally determined set of significant internal controls through completion of an annual controls assessment document. Responsibility for fulfilling this reporting requirement lies with the managing directors and controllers. This document is reviewed by the Business Compliance team who provides feedback and guidance on how to improve existing processes to fill possible gaps in controls.
In addition to the above-described self-assessment of control environment, approximately 90 percent of the legal entities/units had their significant internal controls reviewed or tested in 2017. Internal Audit visits covered over one-third of the operational entities and around 73 percent of third party revenue. The remaining entities were either visited/tested by Business Compliance or conducted self-testing of their local controls. Self-testing results were reviewed by Business Compliance. Remediation of the control deficiencies is the responsibility of the Managing Director of the legal entity, and Internal Audit or Business Compliance makes a control review after the entity has corrected control weaknesses.
Communication
The Controller’s Manual, together with reporting instructions, control register and policies, are stored in the Konecranes intranet for access by personnel. The Group, business areas and regions also arrange meetings to share information on financial processes and practices. Information for the Group’s stakeholders is regularly communicated via the Konecranes Group’s website. To ensure that the information provided is comprehensive and accurate, the Group has established a set of external communication guidelines. These define how, by whom, and when information should be issued; and they are designed to ensure that Konecranes meets all its information obligations and to further strengthen internal controls related to financial reporting.
During 2017
The main activities for 2017 were related to the integration of acquired MHPS business to Konecranes. Financial internal controls were reviewed and aligned between the two different environments to the extent possible. Acquisition also brought a Business Compliance team to the Group, which enabled a significant part of the entities to have their controls tested. Additionally, resources of the Internal Audit team were substantially increased.
Konecranes also continued its IT system project to further develop and implement harmonized processes, increase operational visibility, and improve decision making, and to reduce the overall number of various IT systems. The SAP ERP system is being taken into use for transaction handling and logistics within all three business areas. The Siebel ERP system is being taken into use to manage the field service operations as well as to store the data related to the assets under maintenance contracts.
Konecranes continued the implementation and development of the Financial Shared Service Center (FSSC) concept to offer mainly transaction handling services, financial master data maintenance, and some financial accounting services from regional centers to individual Konecranes companies.
The internal control environment will be improved using common, unified processes and a common system platform. Monitoring the effectiveness of internal controls will become more transparent following the implementation of the SAP ERP system. Financial Shared Service Centers will create a unified framework for transactional processing and provide an enhanced segregation of duties.
Note. This picture will be updated as soon as possible.